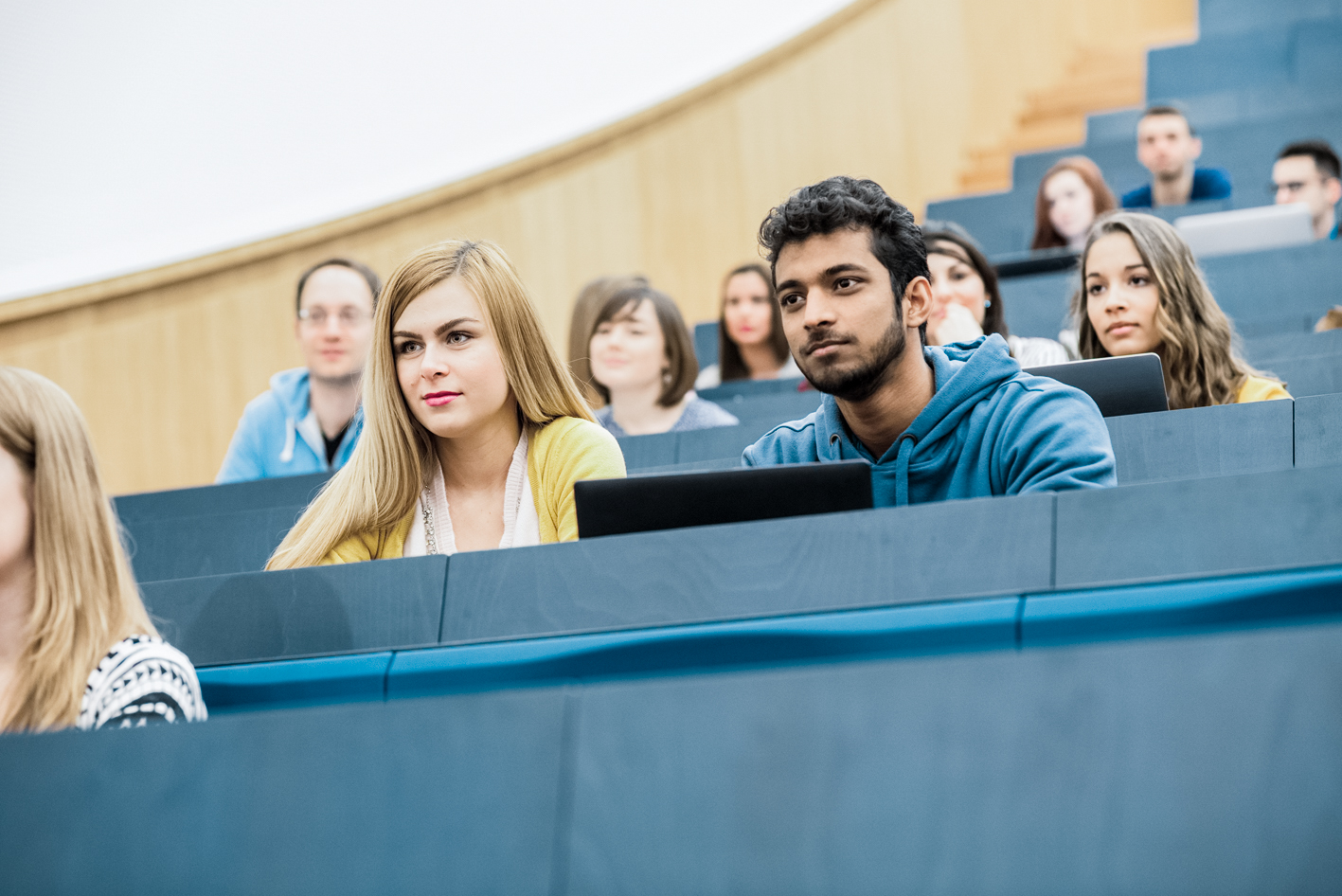
Studying at our University
Find your study programme
- Bachelor’s and master’s programmes Take a look at our range of degrees
- Doctoral schools Find out more about our doctoral programmes
- Specialised studies diplomas Our training offers for future medical specialists
- Continuing education Find out about vocational training & lifelong learning opportunities
Latest news
-

-

-

-
-

-

New open access book unlocks the world of science communication
Outreach, Press Releases, UniversityLearn more
Discover our research
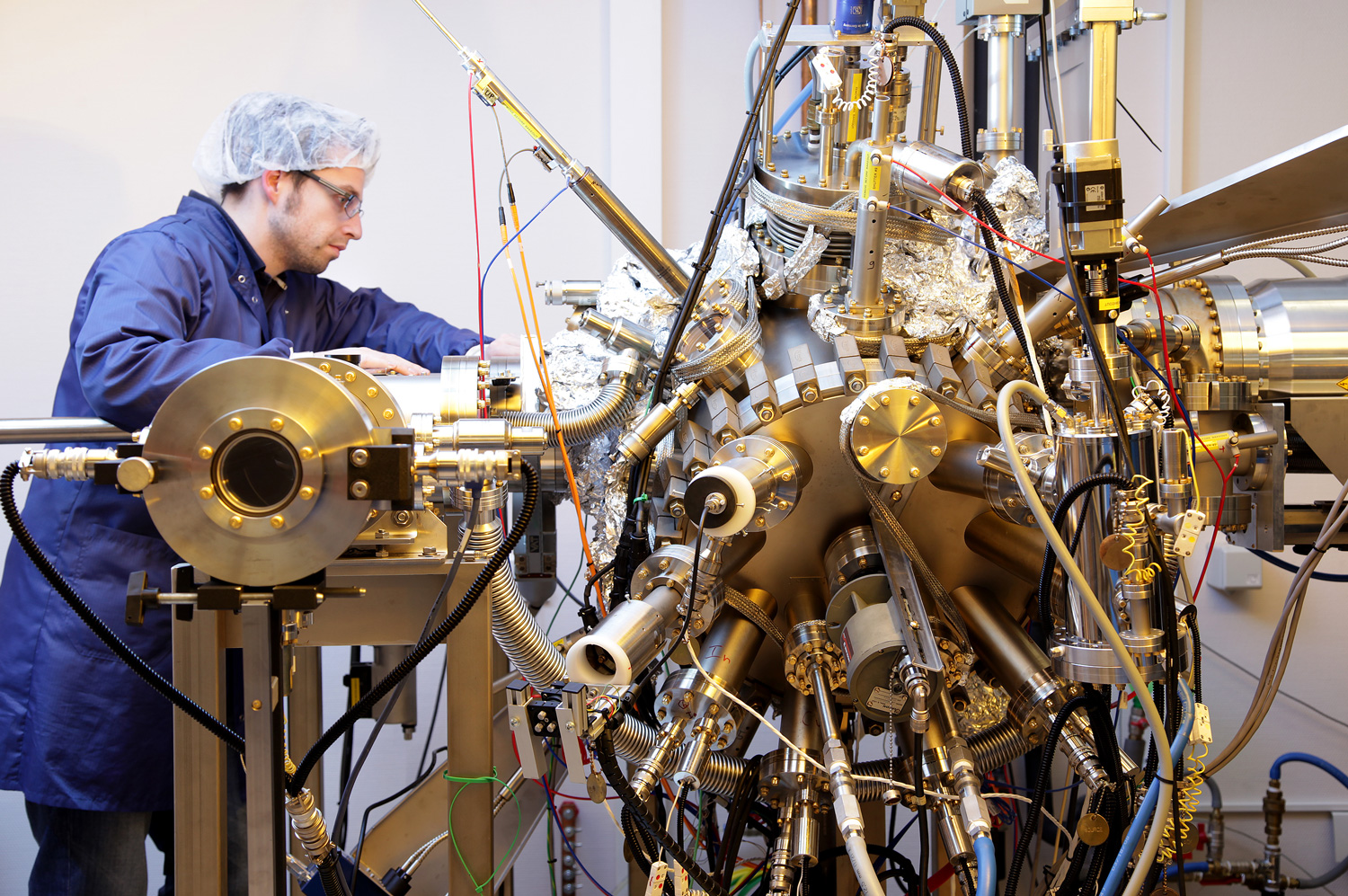
Shaping a digital, healthy and sustainable future
The University of Luxembourg is a world-class research university. It strives for excellence in both fundamental and applied research, and in education. It drives innovation for society, has a high proportion of graduate students, and combines research, teaching and societal impact.
Call for candidates
-

-

Appel à candidatures : Directeur fondateur /Directrice fondatrice du Centre Interdisciplinaire en Droit Européen
UniversitéLearn more




